What are the tonsils and what are they for?
The tonsils, its about extensions of lymphoid tissue that we found located in the pharynx. They constitute the well-known Waldeyer ring, where the lymphocytes quickly come into contact with the different pathogens that may have penetrated both the nose and the mouth. Basically they consist of an accumulation of lymphatic tissue which are located on both sides of the throat.
In the case of the most popular are also known by the name of tonsils or medically with the correct name of palatine tonsils, although did you know that we also have other types of tonsils? In fact, depending on where the tonsils are they actually receive different names.
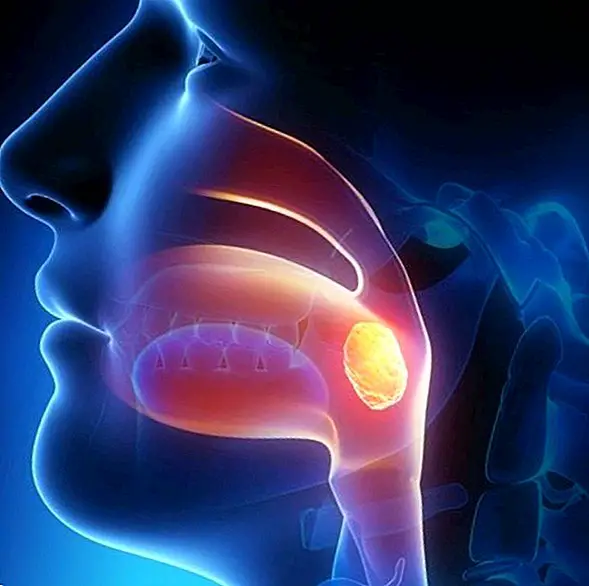
So, for example, we can find the pharyngeal tonsil (or Amygdala of Luschka) located on the roof of the pharynx and that in children it is common for them to be hyperatrophied; the palatine tonsil (or tonsil) located on both sides of the isthmus of the fauces, at the entrance of the oropharynx; the tubal amygdala (or Amygdala of Gerlach) located around the pharyngeal end of the Eustachian tube; and the lingual tonsil, set of lymphoid tissue located at the base of the tongue.
The palatine amygdala is what is also known by the name of angina, especially when there is an infection and subsequent inflammation in the form of tonsillitis.
The main functions of the tonsils
They consist of two masses that we find located in the back of the throat, near the entrance of the respiratory tract where they are precisely able to trap the different and different germs that cause the infections. And that is, above all, one of its main functions: to protect our body against infections caused by viruses and bacteria.
In fact all have a strategic location, thus becoming the first group of defense against all those germs that we have ingested or inhaled.
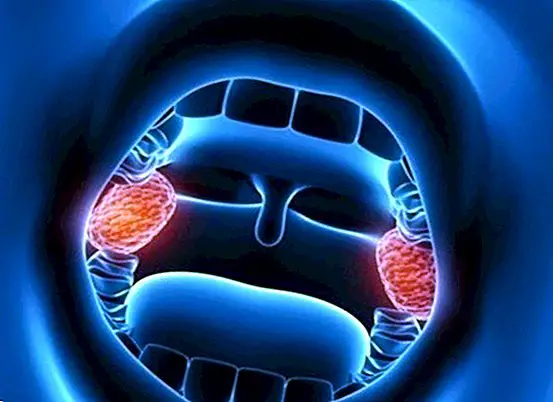
This is because, as many scientists believe, the tonsils are part of our immune system, being able to filter out germs that try to invade our organism, and in turn help development of useful antibodies against germs.
Here are the 3 important functions developed by the tonsils:
- Immune function: They are useful for the defense of our body because they act in order to trap bacteria, germs and antigens that have entered our body, allowing our body to produce antibodies against them. That is, they provide local immunity.
- Production of antibodies: The tonsils are capable of producing antibodies, which help to neutralize viruses and germs that enter our body through the mouth and nose.
- They process the lymphatic tissue: Together with other lymphatic tissues, the tonsils process lymphatic fluid which is distributed in the tissues of the lymphatic system, transporting the immune cells to and from the lymph nodes, and playing an important role in the filtration and destruction of germs.
According to an article published by the Oklahoma Medical Research Foundation, it appears that the palatine tonsils produce 5 specific types of antibodies to fight poliovirus, diphtheria toxoid, staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus pneumoniae and haemophilus influenzae.
Interestingly, this function is of vital importance during the first years of life, which is when it is performed. However, as the years go by and as the child grows, this importance disappears little by little. That is to say, intervene in an important way in the defense of our body and the fight against the disease in the early stages of life, but little by little they stop having this mission.
What's more, with the passage of time they can become a cause of chronic disease, and not only stop fulfilling its defensive mission of our body, but become a source of problems, at which time it is considered the tonsillectomy, or surgery of the tonsils for its removal.



