What is the liver, what is it for and main functions
The liver It is one of the most important organs of our body, due fundamentally -as we will know throughout this note- to the large amount of important functions It takes place throughout the day, and that allows us to greatly enjoy good health.
Given its importance, it is essential to follow a series of guidelines or habits that help when take care of the liver, a question that - to a great extent - helps the follow-up of a healthy diet, rich in fresh fruits and vegetables, avoiding alcohol and the excessive consumption of some drugs, big enemies of the liver. In addition, it is especially useful purify the liver At least once a year.
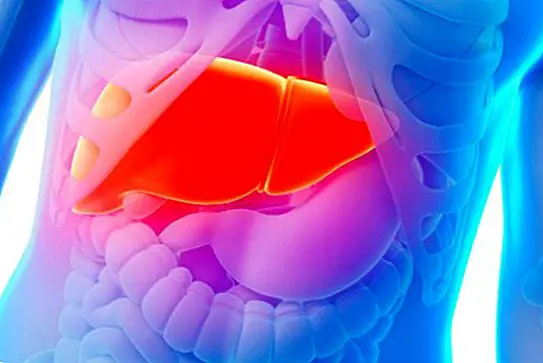
Anyway, among the diseases that today most commonly affects this body is known as fatty liver, so common today with the increase of overweight and obesity, which increase each year dangerously.
What is the liver?
The liver is a fundamental and important organ of our body, mainly due to each and every one of the functions performed, carried out or in which it participates or intervenes. We found it located under the diaphragm, specifically on the right side, although it tends to traverse the abdominal cavity longitudinally.
It is formed by a right lobe and a left lobe. At a microscopic level, it is formed by lobules that are small functional units that are fundamentally responsible for some of their important functions. In addition, we find hepatocytes, which are the main cells of the liver.
In addition, it receives blood through the hepatic artery (which supplies the blood that comes from the heart), and through the portal vein (which transports the blood that is finally sent from the intestine). Once the blood reaches the liver, its different veins are responsible for evacuating it.
What are the main functions of the liver?
Nitrogen metabolism
- Interconversion of non-essential amino acids.
- Gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis during periods of fasting.
- Production of urea from the nitrogen of the amino acids.
- Catabolism of puré passes.
- Catabolism of pyrimidic bases.
- Synthesis of plasma proteins.
Metabolism of carbohydrates
- Synthesis, storage and mobilization of glycogen.
- Store and release sugar to the blood (depending on the different needs of the body).
- It controls the levels of sugar in the blood.
- From precursors such as amino acids, glycerol and lactated gluconeogenesis.
- Hepatose catabolism.

Fat metabolism
- Synthesis of fatty acids and triacylglycerides.
- Stores the fats provided by the different foods consumed.
- Synthesis and catabolism of cholesterol and bile acids.
- Oxidation of fatty acids.
- Production of ketone bodies during breakfast.
- Production of cholesterol to make bile salts.
Other important functions of the liver
In addition to the metabolic functions indicated above, we must also add the following functions:
- Bile secretion
- Metabolism of bilirubin.
- Biosynthesis of the heme group.
- Production of blood plasma proteins.
- Transformation of toxic ammonia into urea (so that the body can eliminate it through urine).
- Decomposition of hormones so that they can be eliminated.
- Processes alcoholic beverages and some medications or drugs, so they can be eliminated in the urine.
- Removes impurities from the blood.
- Stores iron.
- Stores vitamins A, B12 and D.